Процесс реабилитации алкоголиков чреват множеством сложностей и вызовов, как для самих зависимых, так и
Для обеспечения успешности заместительной терапии крайне важно продолжение поддержки после завершения основного курса лечения.
Жизнь в семье, где кто-то страдает от алкогольной зависимости, представляет собой значительные эмоциональные вызовы
Реабилитационные программы могут быть амбулаторными или стационарными, каждый из которых имеет свои преимущества и
Прежде всего, важно понять, что алкоголизм — это заболевание, которое требует серьезного отношения и
Детоксикация организма от алкоголя является важным этапом на пути к восстановлению после длительного употребления
Алкогольное отравление — серьезное состояние, которое может возникнуть после употребления большого количества алкоголя.
Плинтус не только защищает стены от повреждений и скрывает стыки, но и служит важным
Вскрытие замков двери может стать необходимой услугой для любого человека по различным причинам: от
Выбор между написанием эссе и реферата зависит от многих факторов, включая учебную программу, требования
Недорогие подарки для детей сладкие новогодние обязательно понравятся малышам. Красочные и вкусные наборы в
Использование экологически чистых материалов не только снижает негативное воздействие на природу, но и способствует
Этих городов не было на картах. Их жители давали подписки о неразглашении. Здесь проводили испытания с вирусом лихорадки Эбола
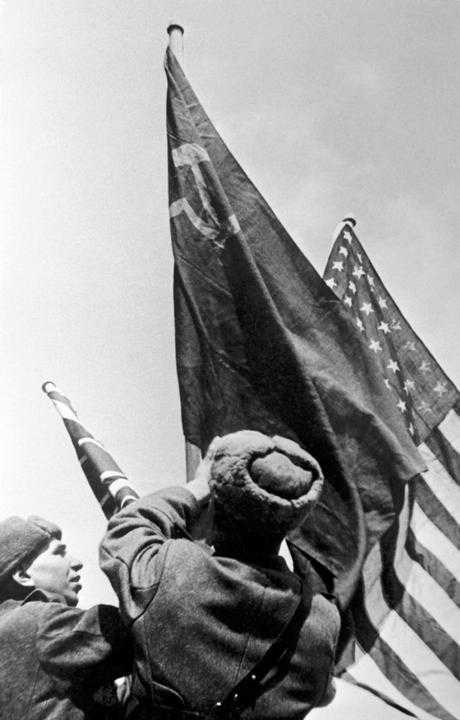
В начале февраля 1945 года в Крыму начались переговоры лидеров стран антигитлеровской коалиции —
Он всегда делает так, как нужно ему, но при этом никогда не был эгоистом.
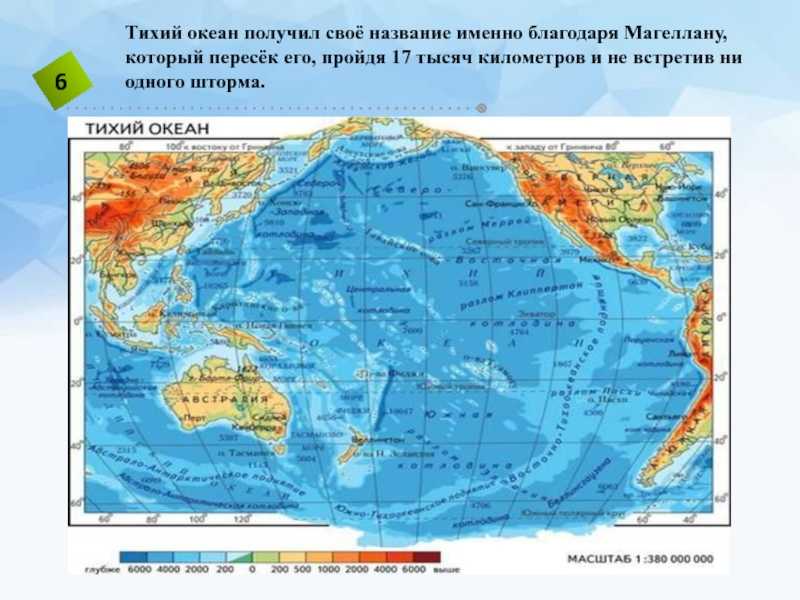
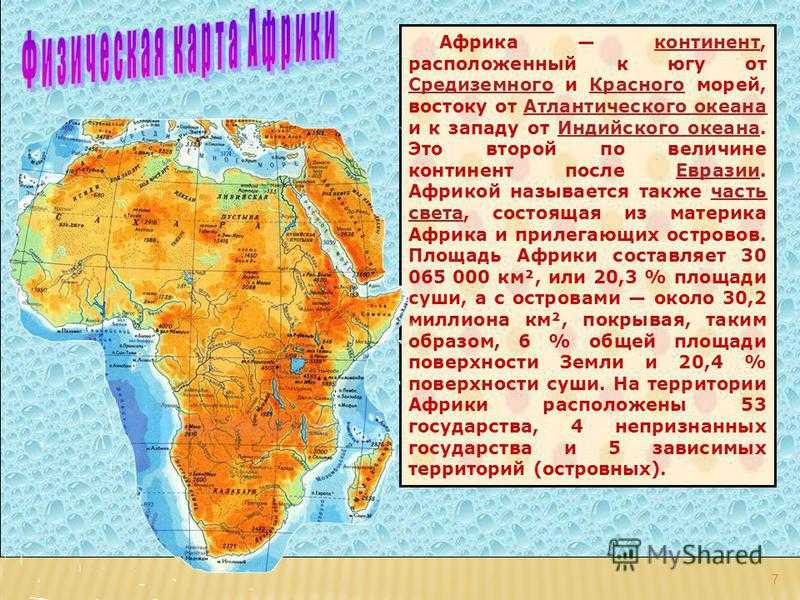
ГАНА 1. В мире существует 196 независимых государств. На территории Африки находится
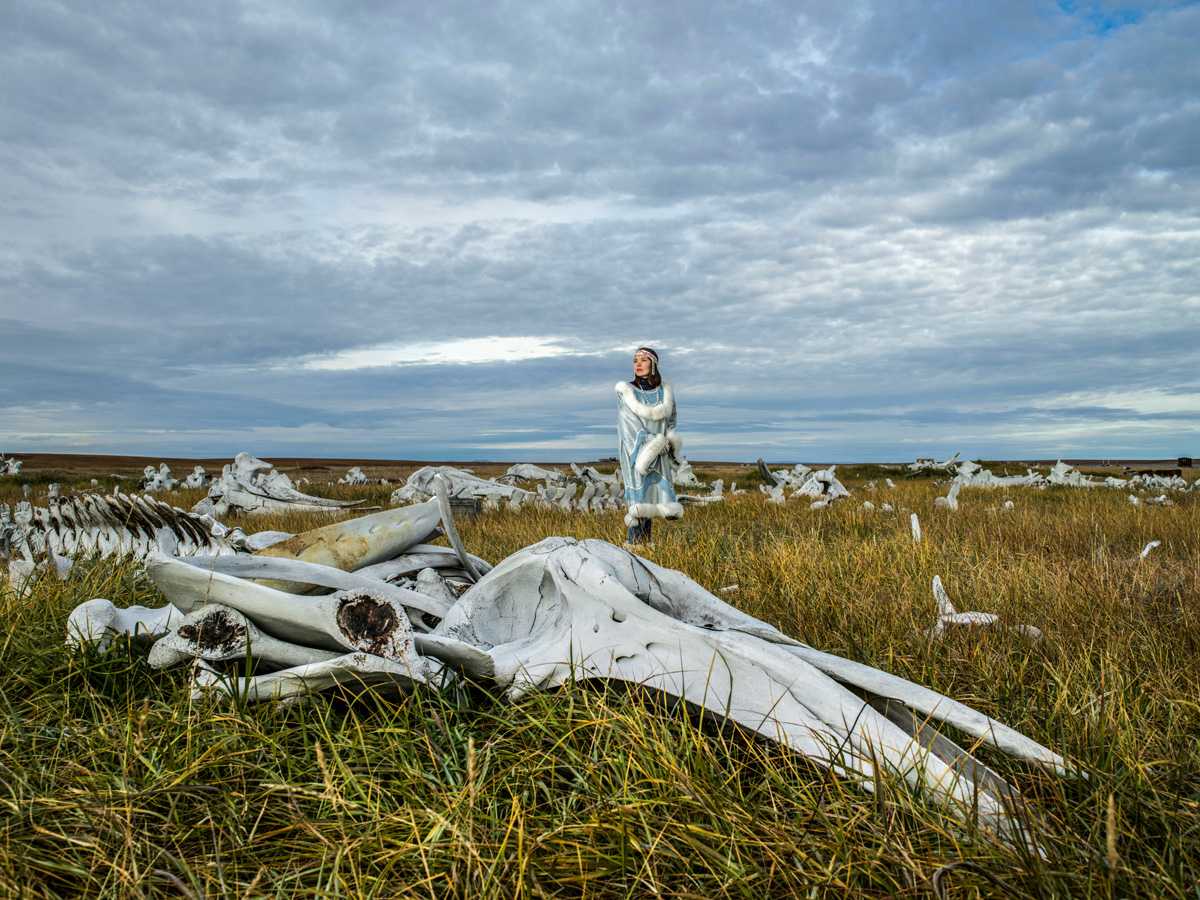
Почему Чукотка считается уникальной и как живет коренное население полуострова - чукчи, эскимосы, эвены,
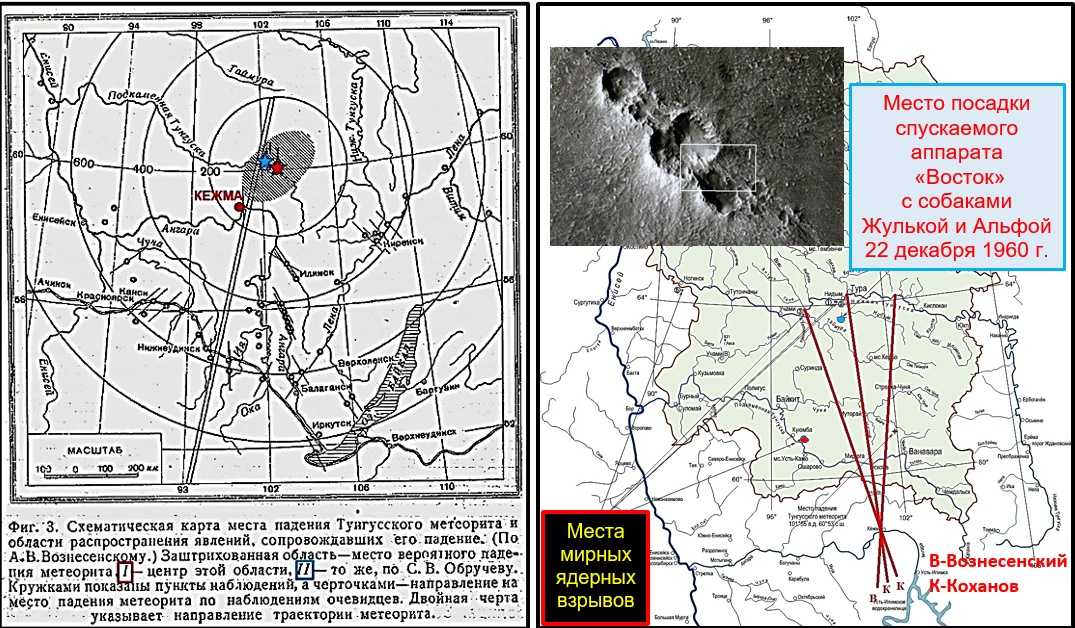
Падение Тунгусского метеорита стало главной загадкой прошлого века, некоторые тайны и интересные факты все
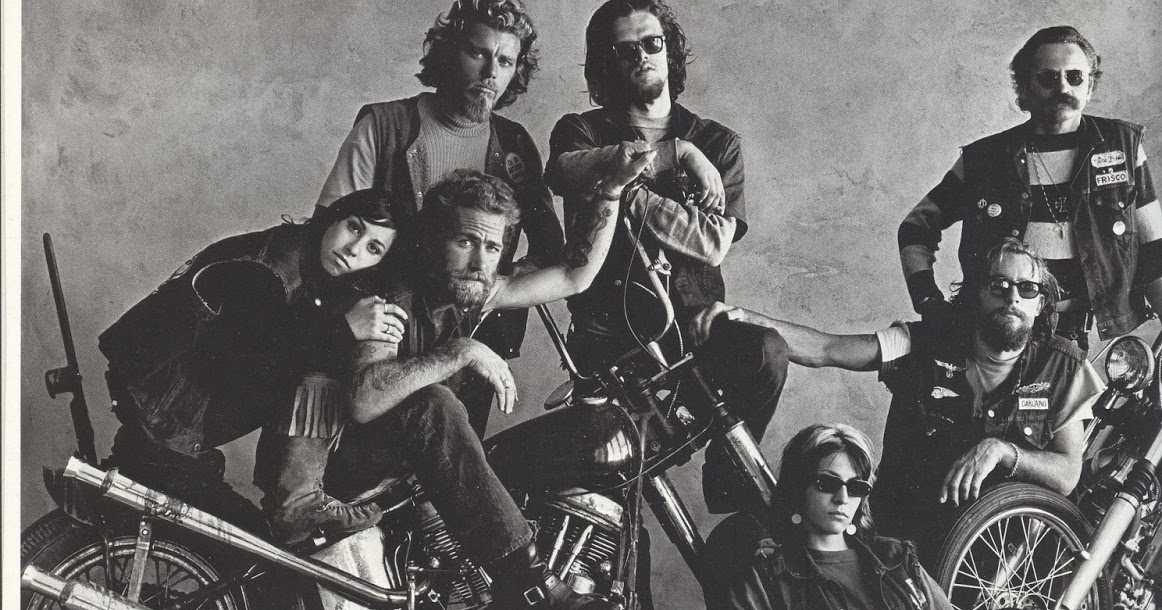
The Rolling Stones и Hells Angels – События того дня, факты и фото, подробная
В данной статье вы рассмотрите ход Тегеранской конференции и ее основные решения.
Поиски Святого Грааля продолжаются и сегодня. В его образе видят и языческий рог изобилия,
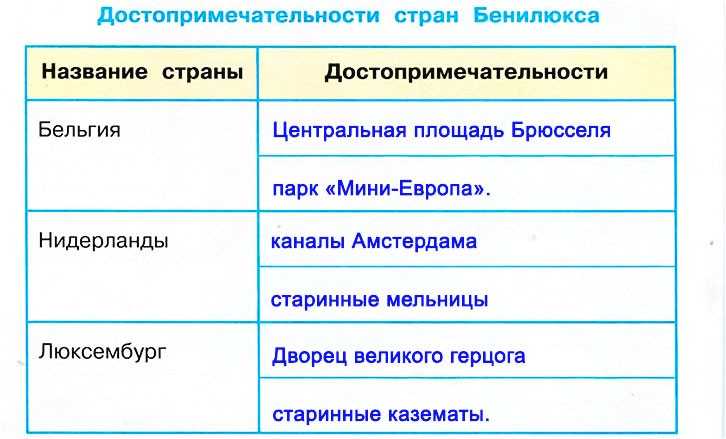
Бенилюкс – это политический, экономический и таможенный союз в Западной Европе, в который входят
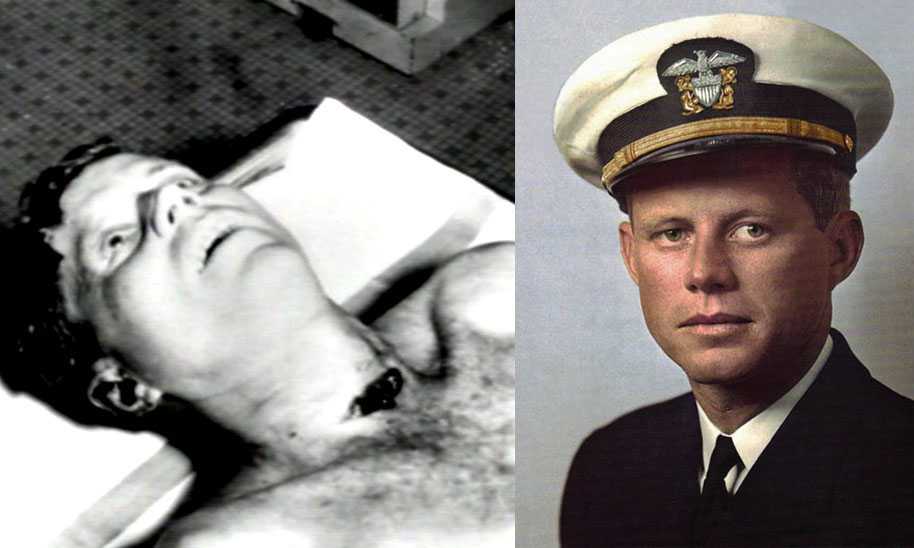
Президента США начали избирать с 1789 года. Должность подразумевает собой наивысший орган исполнительной власти
Какая марка пива является лучшей на российском рынке? Рейтинг популярных брендов с описанием, преимуществами